Booting is the process of starting up a computer or a device. It can also be used as a slang term for kicking someone or something. For example, you can boot your computer when it freezes, or you can boot your annoying roommate out of your apartment. Booting can be fun or frustrating, depending on the context.
Okay, 😂 now let’s actually understand how your computer boots up !!
Compatibility of MBR, GPT with UEFI and BIOS
Before moving on to understand how computers boot we will have to first understand the compatibility of all of the four things above. It’s a bit confusing 🤣😅. I will make points so that you can understand them easily.
- UEFI can boot both GPT and MBR partitioned drives ( CSM required to boot MBR )
- BIOS can boot only MBR partitioned drives
UEFI requires the use of a GPT partitioned drive for booting but has a feature called CSM ( Compatibility Support Module ) that allows you to boot from MBR partitioned drive.
BIOS on the other hand can only boot MBR drives and doesn’t recognise GPT whatsoever.
Booting
Booting is a complex sequence of steps involving hardware and software components working together to load the operating system into the computer’s main memory (RAM).
Once the OS loads into the memory it’s over 😂 you will run your computer as usual. Booting is the process of loading the Operating System into the main memory of a computer and passing the execution process to it, giving the OS kernel complete access to the hardware components of a computer.
Steps of Booting up a Computer:
- Initializing the BIOS or UEFI Firmware
- Finding the Boot drive
- Running Boot Loader
- OS Kernel Taking the ownership
Above are the 4 steps that happen when your computer is powered on or when you press the power button on your PC 😁.
Initializing the BIOS or UEFI Firmware
We all know about BIOS ( Basic input/output system ) and UEFI ( Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) these are the basic firmware that is loaded into the main memory of a computer when it is first powered on.
These Firmware are stored in a ROM located on motherboards. When the computer first boots up it follows its boot routine. Boot Routine commands the CPU to load the program stored in ROM ( BIOS or UEFI ) to its main memory.
Power-on self-test
After loading into the main memory BIOS/UEFI perform a Power-on self-test. Testing all the hardware components for any fault. If any fault is found the booting process stops right away.
From here the booting process is different for GPT and MBR partitioned hard disks.
Finding the Boot drive
After the BIOS or UEFI is loaded into the main memory of the computer it starts to locate a bootable drive to boot from. By drive I mean the actual hard drive that you have in your pc. It checks each drive for bootable parts to continue the booting process.
Finding Bootable Drive in MBR
In MBR the magic number ( boot signature ) tells if the drive is bootable or not.
Finding Bootable Drive in GPT
In GPT the UEFI looks Partition Entry Array for a partition called EFI System Partition ( also called ESP ). EFI partition is created in the GPT partitioning scheme when the drive contains an Operating system and is bootable.
Executing boot process for MBR or GPT
The booting process differs for MBR and GPT which is why I have created a separate section for both.
Please go and have a look into both of them but first, read the 4th step carefully !!
1. Booting from MBR
2. Booting from GPT
OS Kernel Taking the ownership
After the BIOS transfers the execution to the bootloader, the bootloader creates a stable environment for the OS kernel to load. Like loading all the necessary directories and files required by the Kernel. Then the execution is passed to the Operating System’s Kernel after which all the handling is done by the OS itself. Now your Operating System is loaded successfully.
Booting from MBR
MBR contains information about the partitions on a disk and a small program called a boot loader.
MBR is structured in the form of a table going from up to down containing several necessary information about the hard drive.
Structure of MBR
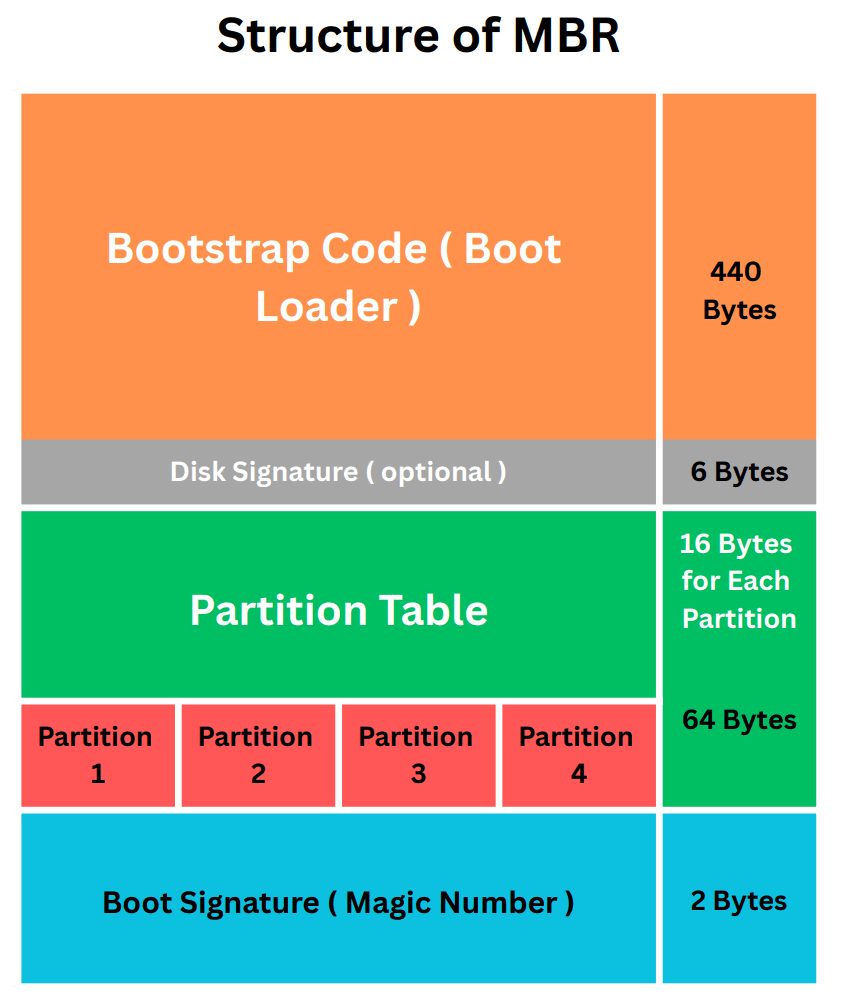
The boot loader is responsible for loading the operating system from one of the partitions. MBR can be used with both Legacy BIOS and UEFI systems, but there are some limitations. For example, MBR can only support up to four primary partitions and up to 2 TB of disk size.
Learn more about GPT: What is MBR, it’s Working and Hacking !!
Steps to Boot from MBR
- When you turn on your computer, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) performs some initial checks and tests on the hardware components. ( Power-on self-test )
- The BIOS then reads the first sector of the disk (the MBR) and executes the boot loader code if the magic number contains 0x55 and 0xAA byte.
- The boot loader scans the partition table and locates the active partition (the one that contains the operating system).
- The boot loader loads the first sector of the active partition (the Volume Boot Record) and transfers control to it.
- The Volume Boot Record loads the operating system kernel and other files into memory and starts the operating system.
Booting from GPT
GPT stands for GUID Partition Table, and it is a newer standard for disk partitioning that overcomes some of the limitations of MBR. GPT uses a globally unique identifier (GUID) for each partition, and it can support up to 128 partitions and up to 9.4 ZB of disk size. GPT also has a backup copy of the partition table at the end of the disk, which makes it more reliable and recoverable.
Structure of GPT
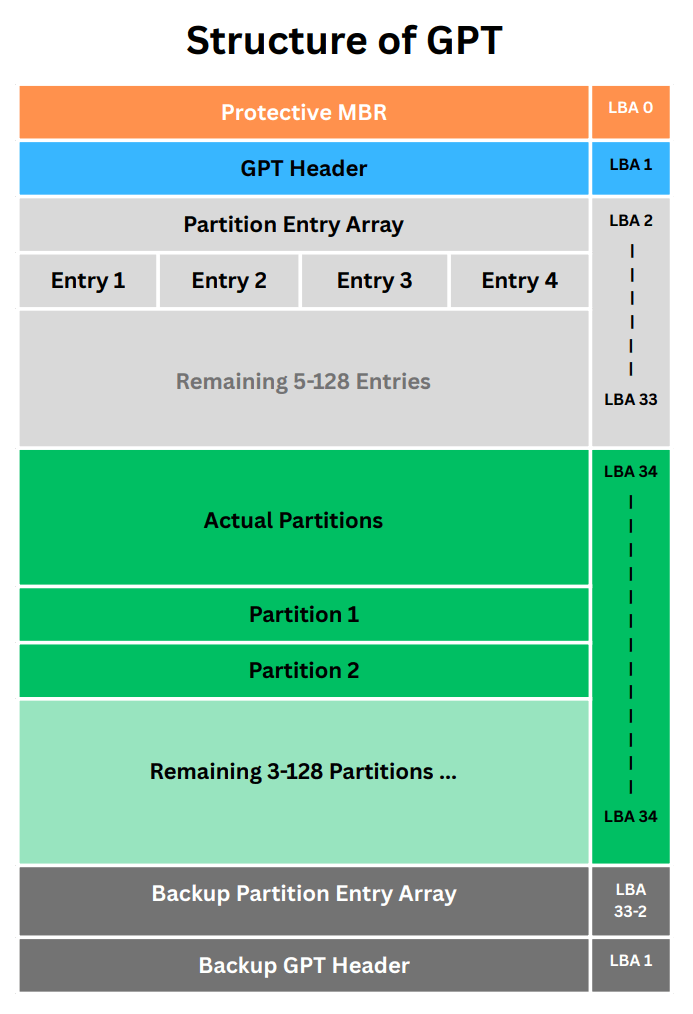
Learn more about GPT: What is GPT, its Structure and Working !!
Steps to Boot from GPT
- When you turn on your computer, the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) performs some initial checks and tests on the hardware components. ( Power-on self-test )
- UEFI then reads the GPT header moves to the partition entry array and locates the EFI System Partition (ESP). ESP is a special partition that contains bootloaders for different operating systems.
- The UEFI loads the boot loader from the ESP and displays a boot menu where you can choose which operating system to boot. ( you don’t see a boot menu with a Windows boot manager, you can see the boot menu with GRUB or any other boot loader that shows a boot menu )
- The boot loader loads the operating system kernel and other files into memory and starts the operating system.
Conclusion
We’ve explored the different ways PCs boot with MBR and GPT in UEFI and BIOS firmware. It’s important to understand these processes to ensure compatibility and stability for your system. Going with the modern GPT and UEFI setup offers benefits like larger disk sizes, enhanced security, and improved performance.
So, if you’re looking to upgrade or build a new system, opting for UEFI and GPT is definitely worth considering. It allows you to take advantage of advanced features and a more flexible boot process. Remember to back up your data before making any conversions, and don’t hesitate to seek assistance if needed.
What is booting in Hindi?
बूटिंग एक प्रक्रिया है जिसमें आपके कंप्यूटर या डिवाइस को शुरू करने के लिए उपयोग की जाती है। यह प्रक्रिया शुरू होती है जब आप अपने सिस्टम को चालू करते हैं और उपकरण सिस्टम के मेमोरी में स्थित सॉफ्टवेयर और ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम को पढ़ने और उसे लोड करने की क्रिया होती है। बूटिंग के दौरान, सिस्टम के हार्डवेयर कंपोनेंट, जैसे कि मदरबोर्ड, प्रोसेसर, और मेमोरी, की स्थिति जांची जाती है और उपयोगकर्ता के लिए एक प्रारंभिक स्थिति बनाई जाती है |
What is booting for classes 2 and 3?
Booting is like waking up a computer or device. When you turn it on, it goes through a special process called booting. It checks if all the parts inside, like the brain (processor) and memory, are ready to work. Then, it starts loading all the important programs and software it needs to work properly. It’s like getting the computer ready for you to use and have fun with!
What is booting and an example?
Booting is the initial process a computer or device goes through when it is turned on. It involves checking and preparing the hardware components, loading the necessary software and operating system, and bringing the system to a functional state ready for use.