The term “DMZ” stands for a demilitarized zone, which acts as a protective buffer between two firewalls. It’s like a security checkpoint for incoming network traffic before it reaches the servers inside. This setup is often called a “perimeter network” or “screened subnet”. Setting up a DMZ divides the network into two parts: the Local Area Network (LAN) and the DMZ itself. Unlike the LAN, which is only accessible within the organization, the DMZ can be reached from outside via the Wide Area Network (WAN). This separation helps in securing networks by adding an extra layer of defence against potential threats.
Purpose of DMZ Network
The purpose of a DMZ network is to provide an additional layer of security for the internal network. In this setup, only designated DMZ hosts can be accessed from the external network. These DMZ hosts have limited access to the internal network, ensuring that if one of them is compromised, the impact is contained and does not spread to the rest of the network. This separation helps reduce the potential harm caused by security breaches, making the network more resilient and better protected overall.
Let’s say you want to host a Minecraft Server to have a little fun time with your friends. You hosted a Minecraft server with DMZ configuration, and suddenly the server you just created got hacked. Now what? What is going to happen with the other devices on your network? Since you used DMZ the rest of the devices on the network remained safe and only your Minecraft Server Device was compromised.
Now imagine the damage that might have happened if you didn’t have used the DMZ config. This is what DMZ is used for 😁.
Where is DMZ Used?
The services listed below all require connectivity to both external and internal networks. A DMZ server is well-suited for managing these services because it can effectively segregate external-facing traffic from internal resources.
Placing the DMZ server between the external and internal networks ensures controlled access and enhances security by limiting the exposure of internal assets to potential threats originating from the external network. This setup enables the DMZ server to facilitate communication with external entities while safeguarding the integrity of the internal network.
- Web servers
- Email servers
- Proxy servers
- Reverse proxy servers.
Design of DMZ Server
There are 2 ways to design DMZ Servers. Now to design a DMZ Network, you can do it physically or logically, which means you can physically add separate firewall routers, cables etc. Or you can do it with just one single device and separate the LAN and DMZ programmatically.
1) The Cheap Way
2) The Expensive Way
The Cheap Way
In this way, we only use one firewall something like this.
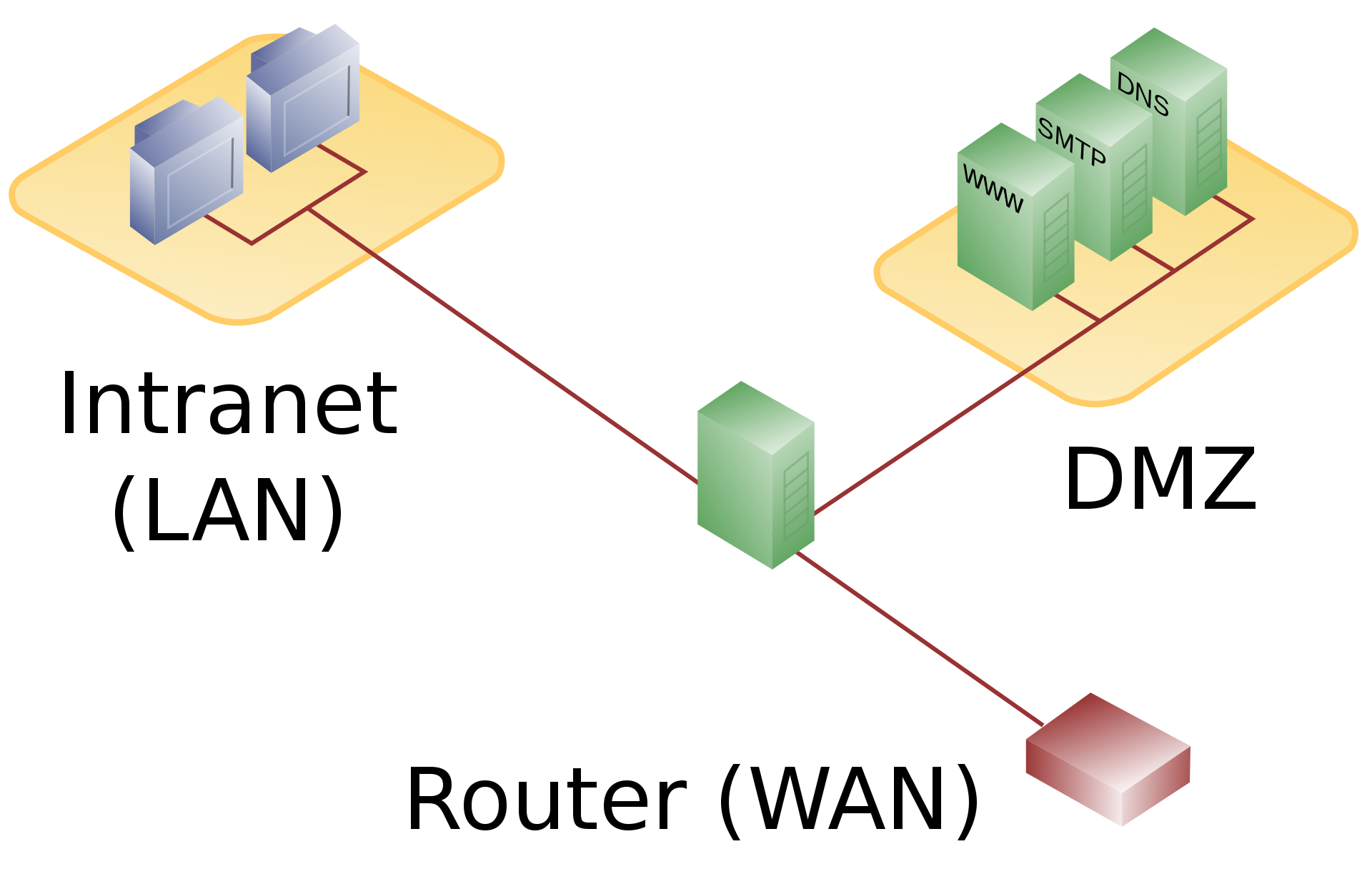
As you can see the first point of interaction is the router that is connected to WAN and then the data is sent to the firewall which separates the internal data and DMZ data.
The firewall allows connections between DMZ and LAN but with increased restrictions to suscept any malicious activity.
The Expensive Way
This is, obviously, more secure and more costly because it uses two firewalls.
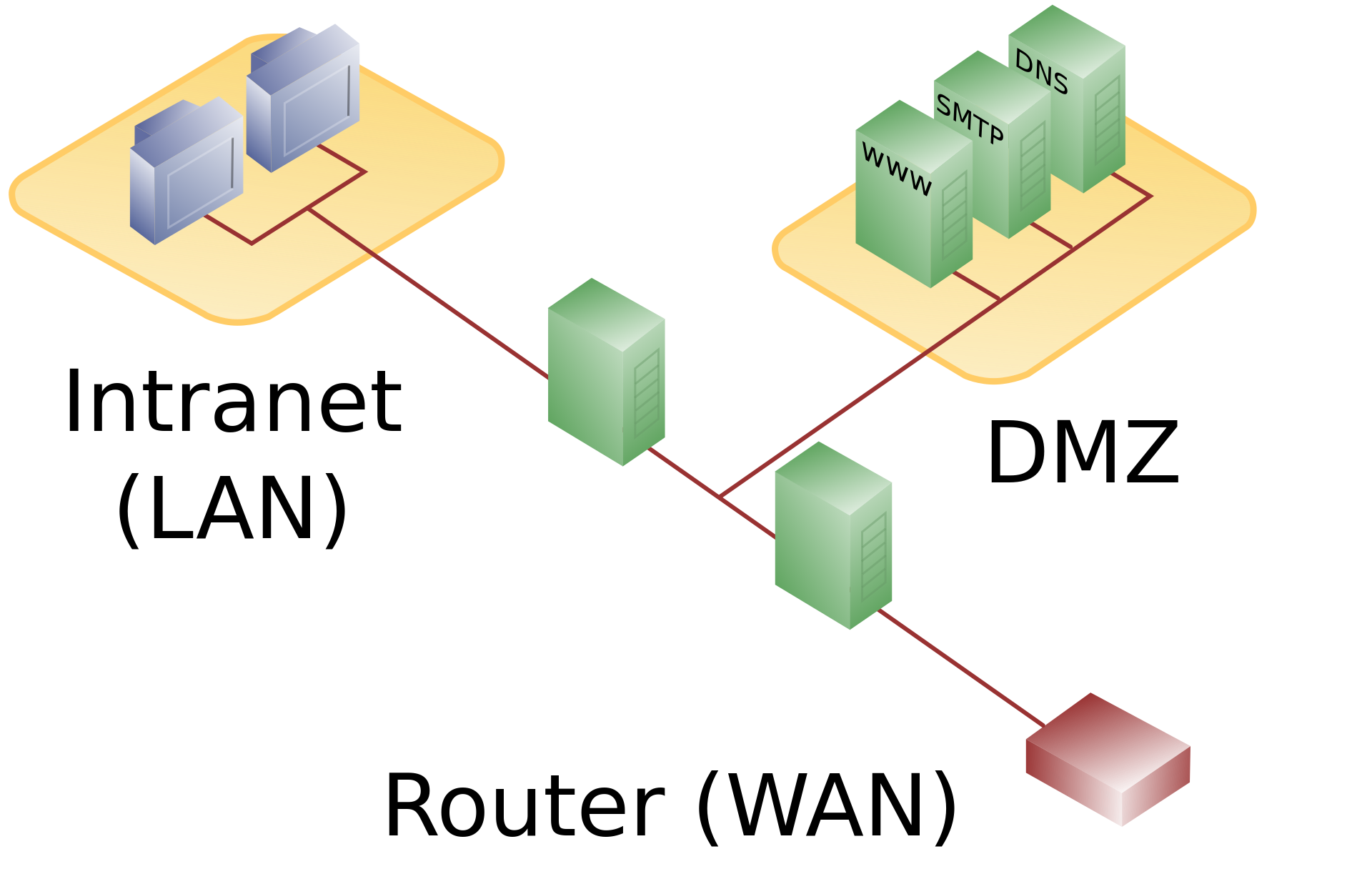
Here the first firewall is also called front-end firewall or perimeter firewall. The first firewall allows connections to the services running on DMZ.
DMZ can also access LAN but with increased security and restrictions because DMZ itself is exposed to the outer world.
The second firewall is also called a back-end firewall or internal firewall. This firewall handles the internal LAN connections and allows connections to DMZ from the LAN



Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve be mindful your stuff previous
to and you’re just extremely magnificent. I really like what you’ve bought right
here, really like what you are saying and the way wherein you are
saying it. You’re making it entertaining and you continue to care for to keep
it smart. I cant wait to learn far more from you. This is really a terrific
website.